How Is AI Used In Dermatology?
Artificial intelligence (AI) has emerged as the major research frontier in computer science.
Although AI has been used in many scientific fields, its use in dermatology is relatively new and limited. Dermatologists must have substantial knowledge of AI concepts because skin conditions, with their plentiful medical and dermatoscopic data and images, have the prospect of being the next large subject in the use of artificial intelligence in medicine.
Studies in artificial intelligence have already been conducted on skin disorders such as skin cancer, psoriasis, dermatitis, and candidiasis.
This article provides an overview of artificial intelligence (AI) and innovations pertinent to anesthesiology, evaluating both existing apps and future potential.
Terminologies of Artificial Intelligence
AI and machine learning strength over the last two decades as a result of improved hardware and software technologies have led us to face the possibility of AI to keep improving present healthcare methodologies.
So, AI research is already ongoing in several medical fields, including dermatology.
However, dermatological AI is still in its early stages compared to some fascinating technical AI applications such as radiology.
With the changing scenario and increased research in dermatological AI, one can anticipate that the use of artificial intelligence in dermatology will tremendously reduce the gap between doctors at various levels of medical facilities and improve diagnostic accuracy.
The Current State of Artificial Intelligence in Dermatology
AI has gradually gained relevance in various fields of dermatology, such as skin cancer, skin conditions, and psoriasis, throughout the last ten years.
AI application in skin cancer
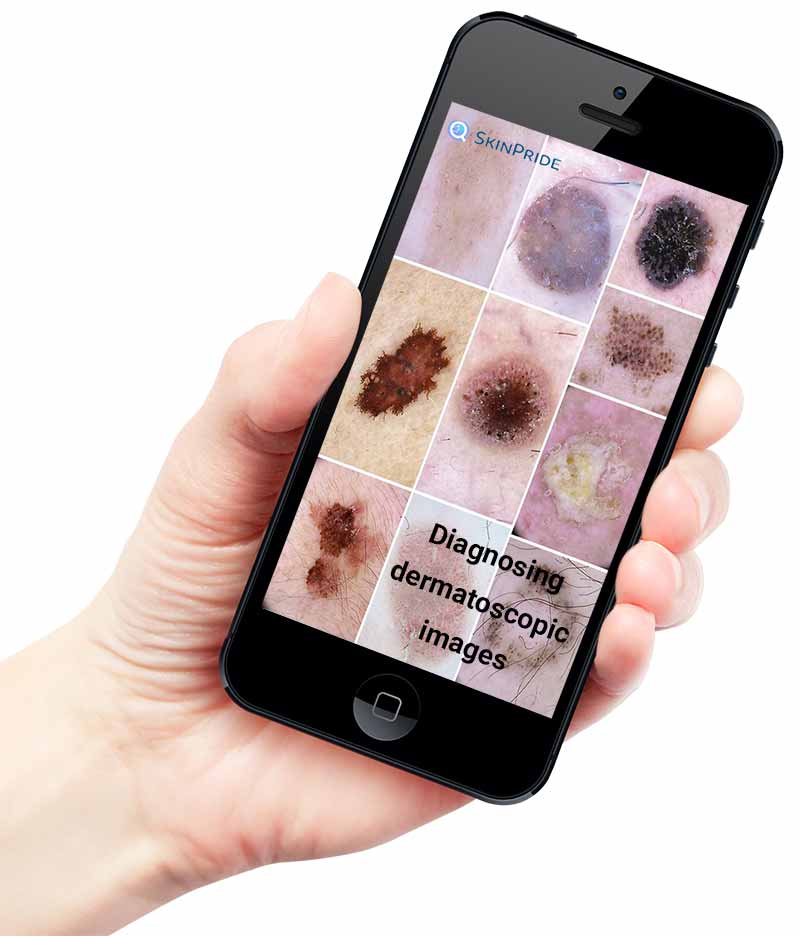
Although it was widely acknowledged applying deep-learning technologies to skin cancer, could improve the high specificity of skin cancer screening too. It was assumed the number of training images required for such a practice could become enormous.

As a result, they concluded that CNN outperformed 11 histopathologists in the classifying of histopathological cancer images, indicating that it has the potential to aid in human melanoma diagnosis.
While the use of artificial intelligence in diagnosing skin cancer across clinical images, dermatoscopic images, and histopathologic images is still in its early stages, it shows great promise.
SkinPride is an AI-powered mobile app that can analyse your skin and introduce the best products for the health of your skin. As a result, you keep healthy, young and far away from skin cancer.